How to write SQL query using chatgpt? – Step 1: Specify the goal or objective of the query writing, Step 2: State the type of operation you want to perform, Step 3: Specify the fields you want to fetch, Step 4: Specify the table or tables from which you want to fetch the data, Step 5: Apply the necessary conditions, Step 6: Add additional clauses if any, Step 7: End the query with proper syntax.
Table of Contents
Advantages of using chatgpt for SQL query writing
ChatGPT is a language model developed by OpenAI. It uses deep learning technique to generate content based on prompt passed to it.
There are various advantages of using chatgpt for SQL query writing viz:
- It is fast: It generates query in seconds,
- Accurate: It generates correct and accurate queries,
- Easy to operate: One just has to pass the prompt in normal human language and it generates SQL query based on that,
- No prior learning is required: As human language instruction is enough for chatgpt, so no prior knowledge of SQL is required,
- Can debug existing sql query and correct it: One can give their existing query and can ask chatgpt to find the error in it,
- Increases productivity: One can write as many queries as they want with chatgpt,
- One can try multiple things on the same query by passing prompts to it,
- Can help in writing complex SQL queries as well.
Disadvantages of using chatgpt for SQL query writing
Chatgpt although write good SQL queries but it has certain issues like it gives correct code syntactically but can have semantic issues or gives irrelevant output for a specific problem.
Other issues associated with chatgpt writing SQL queries are:
- Security concerns:
There are chances of security concerns if one takes the actual data or table name to chatgpt for editing, always use aliases and avoid putting actual data details on chatgpt, - Limited performance optimization:
Chatgpt can generate basic queries, but it may not be able to write complex queries or optimize them for maximum performance, - Inability to handle real time changes:
If some syntax change happens in the database or new function comes in, then chatgpt is will not be able to write queries as per those changes, - Limited or no understanding of business logic:
Chatgpt does not have full understanding of business logics and so it becomes difficult to generate queries that can give desired outcomes.
To write an SQL query using ChatGPT, you can follow these steps:

Step 1: Specify the goal or objective of the query writing
Specify the goal of your SQL query Determine what information you want to retrieve or manipulate from the database. This could be
- Selecting data from a specific table (Select *, Select top 10 * etc.),
- Joining multiple tables (left join, right join, inner join, outer join etc.),
- Performing calculations (sum, subtraction, multiplication, division, mean, median, mode etc.), or
- Updating records.
So, once you decide what is the exact data requirement you can start writing the query in console. Also, become familiarise with data that will help you in joining different tables and solve any errors that may happen.
Step 2: State the type of operation you want to perform
Start the SQL query Begin by stating the type of operation you want to perform. For example,
- If you want to retrieve data, you can start with the SELECT statement,
- If you want to retrieve distinct value of any column then use SELECT distinct column_name statement,
- If you want to see sum of particular column related to some text column then use SELECT text_column, sum(numerical_column) statement etc.
Remember the basic syntax of SQL the chances of error will decrease and will save alot of time – memorise it really well i.e. SELECT > FROM > WHERE > GROUP BY > HAVING.
Step 3: Specify the fields you want to fetch
Specify the columns or fields Specify the columns or fields you want to retrieve or manipulate. If you want all columns, you can use the asterisk (*) wildcard character.
Same thing is mentioned in last step as well the different statements one has to use depending on the requirement i.e. if they want to fetch all the data, specific data, specific columns etc.
If both text and numerical columns are involved then group by is required.
Step 4: Specify the table or tables from which you want to fetch the data

Specify the table(s) Identify the table or tables from which you want to retrieve or manipulate data. You can use the FROM keyword followed by the table name(s).
Specify the schema and table name properly inside FROM statement to fetch the data.
If you want to fetch the data from multiple tables then joins will be required and there are various kinds of joins viz.
- Left join,
- Right join,
- Outer join,
- Inner join and so on.
The JOINS are very important in SQL to do complex calculations i.e. to join multiple tables and retrieve data from them after applying multiple conditions. This is what makes SQL very powerful.
Step 5: Apply the necessary conditions

Add conditions (optional) If you want to filter the data based on specific criteria, you can add conditions using the WHERE clause. This helps narrow down the results.
You can apply multiple WHERE conditions simultaneously – refer this article “SQL Queries with Multiple where condition | SQL मे multiple where conditions कैसे डाले? – Data Analysis Tutorial“ to understand how one can do that.
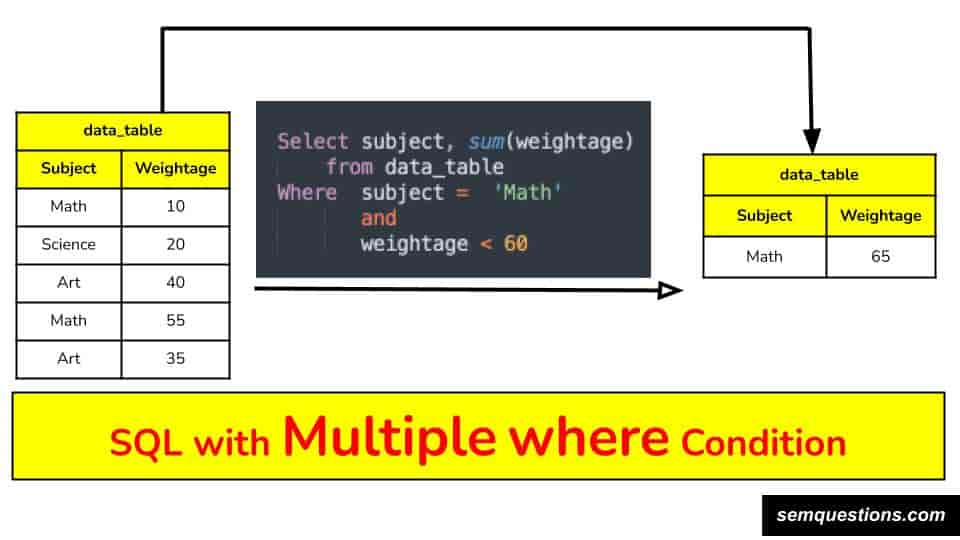
Above screenshot explains an example of SQL with multiple where clause with 1st condition is on numerical column and another on text column.
Step 6: Add additional clauses if any
Add additional clauses (optional) Depending on your goal, you may need to include additional clauses such as
- JOIN (to combine data from multiple tables),
- GROUP BY (to group data based on a column),
- HAVING (to filter grouped data),
- ORDER BY (to sort the results),
- ASC or DESC to sort data in ascending or descending order on a particular field etc.

Above screenshot explains an example of SQL order by numerical column in descending order – refer this article SQL-ORDER BY single/multiple columns ASC and DESC | Data Sorting in SQL for more in-depth understanding of this.
Step 7: End the query with proper syntax
End the query Finish the SQL query with a semicolon (;) to indicate the end of the statement.
Here’s an example of an SQL query to retrieve all records from a table named “employees”:

Keep in mind that the specific syntax and structure of SQL queries may vary depending on the database management system (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle) you are using.
Other related articles:
- SQL command से डेटाबेस में डाटा कैसे सेट करते हैं | How to insert data in DB using SQL Command
- क्वेरी क्या है उदाहरण सहित समझाइए? – Data Analysis Tutorial
- SQL – Wikipedia
Conclusion:
Hope this article was of help for you, do let us know if we can be of help in any other topic.
FAQs
Q1. For retrieving all the records which statement one has to use?
Ans. For retrieving all the records one has to use the SELECT * statement.
Q2. What is the correct SQL syntax?
Ans. SELECT > FROM > WHERE > GROUP BY > HAVING.
Q3. Full form of SQL?
Ans. Structured query language.
Q4. Can ChatGPT write SQL queries?
Ans. Yes, chatgpt is quite powerful to write SQL queries, finding mistakes in queries, giving solution for cases where one is not aware of relevant function to use for querying etc.

2 thoughts on “How to write SQL query using chatgpt?”